最近在测试openEuler发布的用rust写的虚拟化平台StratoVirt,当使用virtio-blk-device设备并且配置1个iothread时,I/O性能竟然比qemu在镜像介质为SSD或者内存盘的情况下性能还要好10%左右,这多少有点让人感到惊讶。 qemu作为一个目前主流的虚拟化模拟器经过全球众多开发人员的优化,性能应该是做的很好了,为什么使用rust写的StratoVirt在这个场景下性能比qemu还要好呢。于是决定深入分析一下qemu的virtio-blk I/O相关代码。
virtio-blk
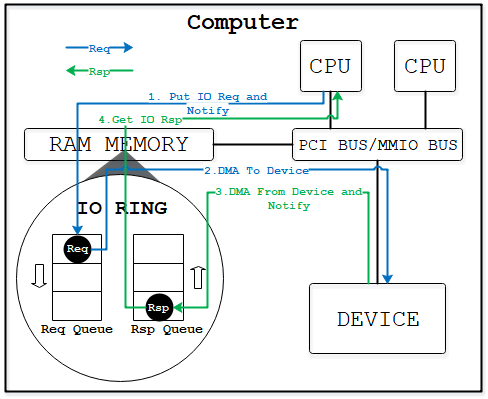
virtio-blk是一种遵循virtio协议规范的block设备,利用共享内存来实现前后端的数据通信。qemu在host侧模拟设备呈现给guest OS,guest OS加载对应的前端驱动。前端驱动将每个IO请求信息填充到descriptor中,更新available ring然后通知后端。后端设备从available ring中取出待完成的IO请求,并往host上真实的物理设备下发IO。物理设备IO完成后,后端填充used ring并通知前端驱动。这样就完成了Guest的IO下发。
代码分析
qemu为virtio-blk设备的每个virtqueue定义了收到guest OS下发IO的通知后的处理回调函数virtio_queue_notify_aio_vq。
static bool virtio_queue_notify_aio_vq(VirtQueue *vq)
{
bool ret = false;
if (vq->vring.desc && vq->handle_aio_output) {
VirtIODevice *vdev = vq->vdev;
trace_virtio_queue_notify(vdev, vq - vdev->vq, vq);
ret = vq->handle_aio_output(vdev, vq);
if (unlikely(vdev->start_on_kick)) {
virtio_set_started(vdev, true);
}
}
return ret;
}
其中的核心函数就是handle_aio_output回调,实际调用的是virtio_blk_data_plane_handle_output。其实际上是virtio_blk_handle_vq函数的简单封装。
bool virtio_blk_handle_vq(VirtIOBlock *s, VirtQueue *vq)
{
VirtIOBlockReq *req;
MultiReqBuffer mrb = {};
bool suppress_notifications = virtio_queue_get_notification(vq);
bool progress = false;
aio_context_acquire(blk_get_aio_context(s->blk));
blk_io_plug(s->blk);
do {
if (suppress_notifications) {
virtio_queue_set_notification(vq, 0);
}
while ((req = virtio_blk_get_request(s, vq))) {
progress = true;
if (virtio_blk_handle_request(req, &mrb)) {
virtqueue_detach_element(req->vq, &req->elem, 0);
virtio_blk_free_request(req);
break;
}
}
if (suppress_notifications) {
virtio_queue_set_notification(vq, 1);
}
} while (!virtio_queue_empty(vq));
if (mrb.num_reqs) {
virtio_blk_submit_multireq(s->blk, &mrb);
}
blk_io_unplug(s->blk);
aio_context_release(blk_get_aio_context(s->blk));
return progress;
}
virtio_blk_get_request从available ring中取出IO请求封装成VirtIOBlockReq,然后调用virtio_blk_handle_request函数将多个请求填充到mrb中。
static int virtio_blk_handle_request(VirtIOBlockReq *req, MultiReqBuffer *mrb)
{
uint32_t type;
struct iovec *in_iov = req->elem.in_sg;
struct iovec *out_iov = req->elem.out_sg;
unsigned in_num = req->elem.in_num;
unsigned out_num = req->elem.out_num;
VirtIOBlock *s = req->dev;
VirtIODevice *vdev = VIRTIO_DEVICE(s);
......
/* We always touch the last byte, so just see how big in_iov is. */
req->in_len = iov_size(in_iov, in_num);
req->in = (void *)in_iov[in_num - 1].iov_base
+ in_iov[in_num - 1].iov_len
- sizeof(struct virtio_blk_inhdr);
iov_discard_back_undoable(in_iov, &in_num, sizeof(struct virtio_blk_inhdr),
&req->inhdr_undo);
type = virtio_ldl_p(vdev, &req->out.type);
/* VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT defines the command direction. VIRTIO_BLK_T_BARRIER
* is an optional flag. Although a guest should not send this flag if
* not negotiated we ignored it in the past. So keep ignoring it. */
switch (type & ~(VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT | VIRTIO_BLK_T_BARRIER)) {
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_IN:
{
bool is_write = type & VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT;
req->sector_num = virtio_ldq_p(vdev, &req->out.sector);
if (is_write) {
qemu_iovec_init_external(&req->qiov, out_iov, out_num);
trace_virtio_blk_handle_write(vdev, req, req->sector_num,
req->qiov.size / BDRV_SECTOR_SIZE);
} else {
qemu_iovec_init_external(&req->qiov, in_iov, in_num);
trace_virtio_blk_handle_read(vdev, req, req->sector_num,
req->qiov.size / BDRV_SECTOR_SIZE);
}
......
/* merge would exceed maximum number of requests or IO direction
* changes */
if (mrb->num_reqs > 0 && (mrb->num_reqs == VIRTIO_BLK_MAX_MERGE_REQS ||
is_write != mrb->is_write ||
!s->conf.request_merging)) {
virtio_blk_submit_multireq(s->blk, mrb);
}
assert(mrb->num_reqs < VIRTIO_BLK_MAX_MERGE_REQS);
mrb->reqs[mrb->num_reqs++] = req;
mrb->is_write = is_write;
break;
}
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_FLUSH:
virtio_blk_handle_flush(req, mrb);
break;
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_SCSI_CMD:
virtio_blk_handle_scsi(req);
break;
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_GET_ID:
......
/*
* VIRTIO_BLK_T_DISCARD and VIRTIO_BLK_T_WRITE_ZEROES are defined with
* VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT flag set. We masked this flag in the switch statement,
* so we must mask it for these requests, then we will check if it is set.
*/
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_DISCARD & ~VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT:
case VIRTIO_BLK_T_WRITE_ZEROES & ~VIRTIO_BLK_T_OUT:
......
default:
virtio_blk_req_complete(req, VIRTIO_BLK_S_UNSUPP);
virtio_blk_free_request(req);
}
return 0;
}
当mbr满或者队列遍历完之后调用virtio_blk_submit_multireq函数将IO请求提交给后端驱动。virtio_blk_submit_multireq实际最终调用了blk_aio_prwv函数。
BlockAIOCB *blk_aio_pwritev(BlockBackend *blk, int64_t offset,
QEMUIOVector *qiov, BdrvRequestFlags flags,
BlockCompletionFunc *cb, void *opaque)
{
return blk_aio_prwv(blk, offset, qiov->size, qiov,
blk_aio_write_entry, flags, cb, opaque);
}
static BlockAIOCB *blk_aio_prwv(BlockBackend *blk, int64_t offset, int bytes,
void *iobuf, CoroutineEntry co_entry,
BdrvRequestFlags flags,
BlockCompletionFunc *cb, void *opaque)
{
BlkAioEmAIOCB *acb;
Coroutine *co;
blk_inc_in_flight(blk);
acb = blk_aio_get(&blk_aio_em_aiocb_info, blk, cb, opaque);
acb->rwco = (BlkRwCo) {
.blk = blk,
.offset = offset,
.iobuf = iobuf,
.flags = flags,
.ret = NOT_DONE,
};
acb->bytes = bytes;
acb->has_returned = false;
co = qemu_coroutine_create(co_entry, acb);
bdrv_coroutine_enter(blk_bs(blk), co);
acb->has_returned = true;
if (acb->rwco.ret != NOT_DONE) {
replay_bh_schedule_oneshot_event(blk_get_aio_context(blk),
blk_aio_complete_bh, acb);
}
return &acb->common;
}
blk_aio_prwv创建了一个协程调用blk_aio_write_entry函数。
static void blk_aio_write_entry(void *opaque)
{
BlkAioEmAIOCB *acb = opaque;
BlkRwCo *rwco = &acb->rwco;
QEMUIOVector *qiov = rwco->iobuf;
assert(!qiov || qiov->size == acb->bytes);
rwco->ret = blk_do_pwritev_part(rwco->blk, rwco->offset, acb->bytes,
qiov, 0, rwco->flags);
blk_aio_complete(acb);
}
blk_aio_write_entry在后端block设备是文件时,最终调用的函数是raw_co_pwritev。当命令行参数指定aio=threads时,raw_co_prw函数会调用raw_thread_pool_submit函数提交下半部任务通知指定事件源所在的线程去创建AIO线程(如果没有空闲线程且AIO线程池线程数没有超过最大限制)。
static void spawn_thread(ThreadPool *pool)
{
pool->cur_threads++;
pool->new_threads++;
/* If there are threads being created, they will spawn new workers, so
* we don't spend time creating many threads in a loop holding a mutex or
* starving the current vcpu.
*
* If there are no idle threads, ask the main thread to create one, so we
* inherit the correct affinity instead of the vcpu affinity.
*/
if (!pool->pending_threads) {
qemu_bh_schedule(pool->new_thread_bh);
}
}
qemu_bh_schedule调用aio_bh_enqueue接口将下半部任务添加到指定的AioContext的下半部任务列表里,然后调用aio_notify接口通知指定事件源所在的线程。
void aio_notify(AioContext *ctx)
{
/*
* Write e.g. bh->flags before writing ctx->notified. Pairs with smp_mb in
* aio_notify_accept.
*/
smp_wmb();
qatomic_set(&ctx->notified, true);
/*
* Write ctx->notified before reading ctx->notify_me. Pairs
* with smp_mb in aio_ctx_prepare or aio_poll.
*/
smp_mb();
if (qatomic_read(&ctx->notify_me)) {
event_notifier_set(&ctx->notifier);
}
}
qemu用AioContext结构体来定义事件源,该结构体里存放了所有加入到这个事件源的fd的事件处理函数、下半部任务列表、事件通知对象notifier等。qemu的事件源分两类,一类是处理各种各样事件的iohandler_ctx,另一类是处理块设备的异步IO请求,可以是主线程的qemu_aio_context,或者是模块自己创建的AioContext。如果配置了iothread,iothread也会创建对应的事件源。block设备通过bdrv_attach_aio_context函数注册指定的事件源。对应线程poll fd收到事件后,会调用aio_dispatch_handler函数来调用处理事件的回调。
当后端驱动完成IO的下发后需要填充virtio的used ring,向guest OS注入中断通知前端驱动。
blk_aio_complete
--> virtio_blk_rw_complete
--> virtio_blk_req_complete
--> virtio_blk_data_plane_notify
--> virtio_notify_irqfd
void virtio_notify_irqfd(VirtIODevice *vdev, VirtQueue *vq)
{
WITH_RCU_READ_LOCK_GUARD() {
if (!virtio_should_notify(vdev, vq)) {
return;
}
}
trace_virtio_notify_irqfd(vdev, vq);
/*
* virtio spec 1.0 says ISR bit 0 should be ignored with MSI, but
* windows drivers included in virtio-win 1.8.0 (circa 2015) are
* incorrectly polling this bit during crashdump and hibernation
* in MSI mode, causing a hang if this bit is never updated.
* Recent releases of Windows do not really shut down, but rather
* log out and hibernate to make the next startup faster. Hence,
* this manifested as a more serious hang during shutdown with
*
* Next driver release from 2016 fixed this problem, so working around it
* is not a must, but it's easy to do so let's do it here.
*
* Note: it's safe to update ISR from any thread as it was switched
* to an atomic operation.
*/
virtio_set_isr(vq->vdev, 0x1);
event_notifier_set(&vq->guest_notifier);
}
在设备不使用MSI/MSI-X或者KVM不支持KVM_CAP_IRQ时,向guest注入中断的回调为virtio_queue_guest_notifier_read函数,其通过ioctl系统调用借助KVM模块实现中断注入的目的。virtio_queue_guest_notifier_read由event_notifier_set_handler函数注册,注入中断的事件被加到了main loop的iohandler_ctx这个事件源里,也就是说IO完成后会通过写eventfd通知主线程,再由主线程来注入中断。
void event_notifier_set_handler(EventNotifier *e,
EventNotifierHandler *handler)
{
iohandler_init();
aio_set_event_notifier(iohandler_ctx, e, false,
handler, NULL);
}
如果是支持MSI/MSI-X中断PCI设备,通过irqfd机制直接将中断通过KVM注入给虚拟机的vcpu。
virtio_pci_set_guest_notifiers
--> kvm_virtio_pci_vector_use
-- > kvm_virtio_pci_irqfd_use
-- > kvm_irqchip_add_irqfd_notifier_gsi
-- > kvm_irqchip_assign_irqfd
总结
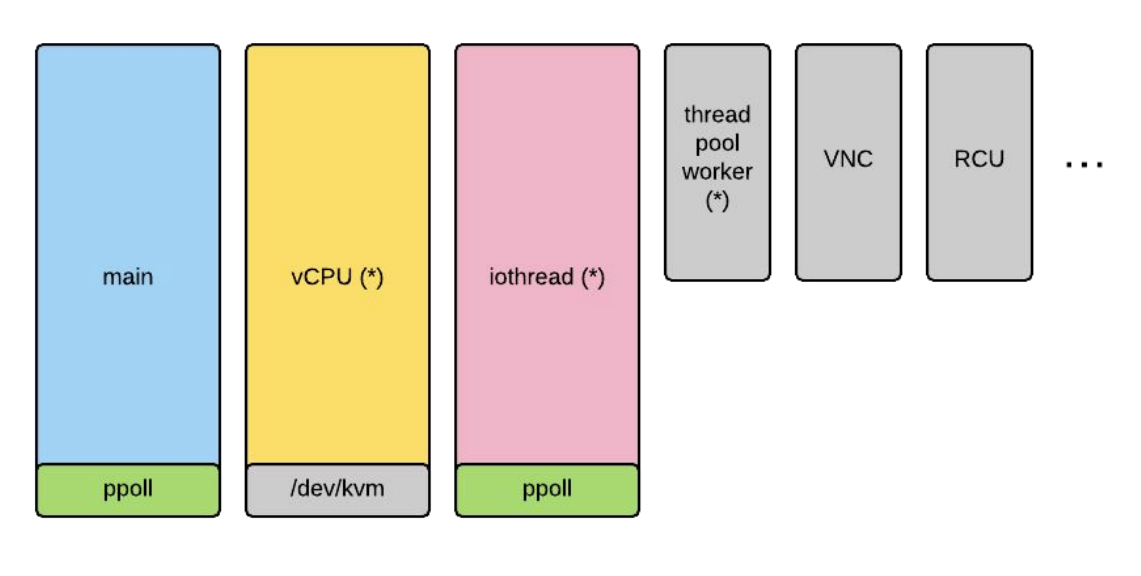
qemu默认有一个主线程,借助glib的事件循环机制实现事件的监听分发。virtio-blk设备配置iothread后,virtio队列请求都会在iothread中的协程中处理,否则就在main loop里。当aio配置为threads时,会创建AIO线程池向后端的驱动下发IO。IO完成以后,对于virtio-blk-device来说需要通知主线程往guest中注入中断。因此,整个流程涉及到很多的线程创建及同步,从测试后抓到的火焰图来看性能的开销还是比较大的。
参考资料
[1] Improving the QEMU Event Loop

